This device connects to your audio input and output video from a cassette player or a camcorder and thus pass through the air to one or more televisions in the area of a house. It is also useful to output the image and the sound of a computer to do multimedia presentations in several TV screens distributed in an enclosure. If you have a satellite TV service or premium cable system and want to watch programming on multiple televisions with a single tuner and / or decoder output can connect it to this project and enjoy the images in the house. Also useful in closed systems for security video, avoiding large number of cable runs.
Domestic TV Transmitter Circuit Diagram
As shown in the circuit diagram the circuit has several stages (a local oscillator, an FM modulator for audio an AM modulator for video, a mixer and an output amplifier) very simple to assemble. It has the controls necessary for achieving optimal fit and proper signal transmission.
Circuit Description:
The video signal entering through connector J1 is finished, firstly, by the resistor R6 and coupled through capacitor C1 to the clamping diode D1. The clamping force sync pulses to a fixed DC level to reduce blooming effect. Potentiometer R3 is used to set the gain of the video signal, its effect is similar to the TV contrast control. The bias control (R7) is used to set the minimum level of the signal, when images are transmitted completely dark. Thus, the TV receiver can efficiently maintain synchronism. As seen below, the potentiometers R3 and R7 are adjusted together for optimal performance in all conditions.
The RF transformer T1 (and its internal capacitor) forms the tank circuit of a Hartley oscillator, which is tuned to 4.5 MHz
The audio signal that enters through J2 is coupled to the base of transistor Q3 through C2 and R4: the audio signal modulates the current at the base of Q3 to form an audio subcarrier that is higher than 4.5MHz frequency of the carrier. The modulated subcarrier frequency is applied to the modulator section through C5 and R9. The resistor R9 adjusts the level of the sub-carrier with respect to the video signal.
Transistors Q1 and Q2 amplitude modulate the audio and video signals on the RF carrier. The operating frequency is set by the coil L4, consisting of 3.5 turns of wire coating 24 on a common way with a ferrite rod. This coil is part of a Colpitts tank circuit also containing C7 and C9. The tank circuit forms a feedback network on Q4, making it oscillate at the frequency set. The RF output of the oscillator section is amplified by Q5 and Q6, whose supply voltage comes from the modulator section. The antenna adapter and low-pass filter is formed by C12, C13, and L1. The resistor R12 is optional, it is used to adapt the output to any type of antenna.
Printed Circuit:
You can use the printed circuit designed by the author, which has plenty of space for both components as well as for the battery clip, space for this subject and the island left to screw the antenna. It is possible, but make a custom PCB with minimum space required, provided that you follow the guidelines of the electrical circuit. In both cases it is advisable to use printed circuit board in place of the phenolic pertinax since the latter absorbs moisture which would cause instability of the system.
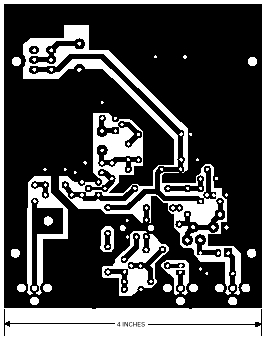
Side tracks (welding) in size. (scale 1:1)
Expanded components distribution.
Notes:
- The 4.5MHz RF transformer (T1) can be anything that fits, provided you have the internal capacitor connected to the secondary.
- L4 must be done manually. Respect the parameters given above.
- If used in resistor R12, to be placed on the solder side of the printed circuit between the antenna output and ground. This component must be installed whenever you use an antenna other than the internal, making a correct fit between it and the circuit.
Adjust:
To calibrate the transmitter will need a TV receiver and a signal source
such as a video recorder or a camcorder. Need, moreover, a non-metallic
tool to adjust the coil L4 and the transformer T1. A new 9v battery can
be used for adjustments, but if calibration is difficult, try doing it
with a 12v power supply. Note that during the adjustment and testing of
the unit, we find that it works much better with a stable supply
filtered 12 volts. If you come to the same conclusion, add a voltage
input connector welding it to the appropriate points on the circuit
board (instead of the battery clip).
Tune the TV receiver in an
unused channel (no transmission) between 2 and 6. The TV must be
connected directly to the internal antenna, an external antenna or a
cable system will not work. Make sure both knobs are in the center
position (at halfway) and apply power to the circuit. Adjust L4 with
non-metallic tool until the TV screen goes blank (rain disappears).
Then, carefully adjust L4 to achieve the best possible reception.
Connect the audio outputs of a VCR and other video source to J1 and J2,
if necessary operate the VCR. You should see the image on the TV screen:
if so, L4 setting up the best picture possible, and if not, check the
circuit board in search of an error in welds or components in the
inputs. Then adjust R3 for optimum brightness and R7 for a general
adjustment of video quality. You may need to make minor adjustments on
L4 after adjusting R3 and R7. Finally, adjust T1 with nonmetallic tool
to get the best audio possible. After that the transmitter is properly
calibrated.

View completed and mounted equipment in your cabinet
Important:
The use of these systems is regulated by law in much of the world. Before operating, we suggest that you consult a competent legal authority on the scope and restrictions of the law regarding the use of these devices. In some countries can cause illegal emissions from confiscation of equipment to the prison of the copyright holder.





























+for+FM+Transmitter.jpg)
+for+FM.png)













